Industry trends
Focus on semiconductor electrical performance testing
location:Home > News > Industry trends
Digital source measure meter refers to a measuring instrument that can be used as a four-quadrant voltage source or current source to provide accurate voltage or current, and can simultaneously measure the current value or voltage value; it can be used as a programmable voltage source or programmable current source when powered ;When used as a multimeter, it can be used as a digital voltmeter (current source, output current is 0, measuring voltage) or a digital ammeter (voltage source, output voltage is 0, measuring current) or a digital ohmmeter (current source, output current is a certain value, Measuring voltage); when it is an electronic load, it can be used as a programmable constant voltage load or a programmable constant current load; when it is a power supply/measurement meter combination (SMU), it can measure current for voltage or measure voltage for current.
source measure meter—— Five meters in one
The domestic S-type digital source measure meter integrates multiple functions such as voltage, current input and output, and measurement. The maximum output voltage reaches 300V, the minimum current resolution is 10pA, and supports four-quadrant operation, so it can be widely used in various electrical characteristic tests: semiconductor Characteristic testing and analysis of IC or components, power devices, sensors, organic materials and nanomaterials.
The following are typical application areas for Source measure unit instruments::
• Nanomaterials and devices
- Graphene
– carbon nanotubes
- Nanowires
– Low power nanostructure
• Semiconductor structures
– Wafer
– film
• Organic materials and devices
– Electronic Ink
– Printed Electronics Technology
• Energy efficiency and lighting
– LED/AMOLED
– Photovoltaic/solar cells
- Battery
• Discrete and passive components
– Dual leads: resistors, diodes, Zener diodes, LEDs, sensors
– Three-lead: small signal bipolar junction transistor (BJT), field effect transistor (FET), etc.
• Analysis of material properties
– Resistivity
-Hall Effect
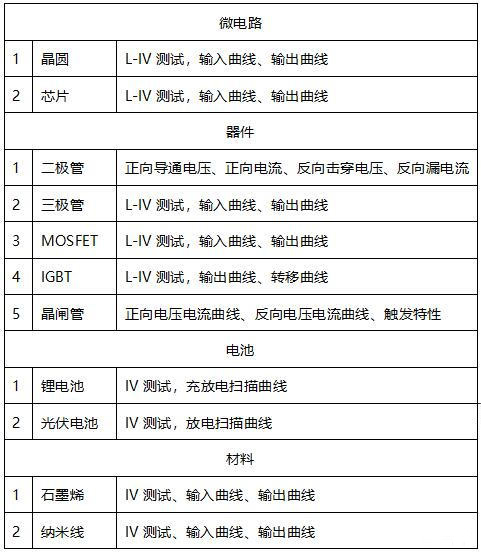
Typical device parameter tests are as follows:
Transistor/Rectifier: Forward Voltage (Vf), Reverse Voltage (Vr), Reverse Leakage Current (Ir)
MOSFET/JFET: output characteristics (Vds-Id), transfer characteristics (Vgs-Id), on-resistance (Rdson), breakdown voltage (BVdss, BVdg), leakage current (Idss, Igss)
Bipolar Transistor/IGBT: Saturation Voltage (Vcesat), Output Characteristics (Vce-Ic), Breakdown Voltage (Vceo, Vebo, Vcbo), Leakage Current (Iceo, Ices, Iebo)